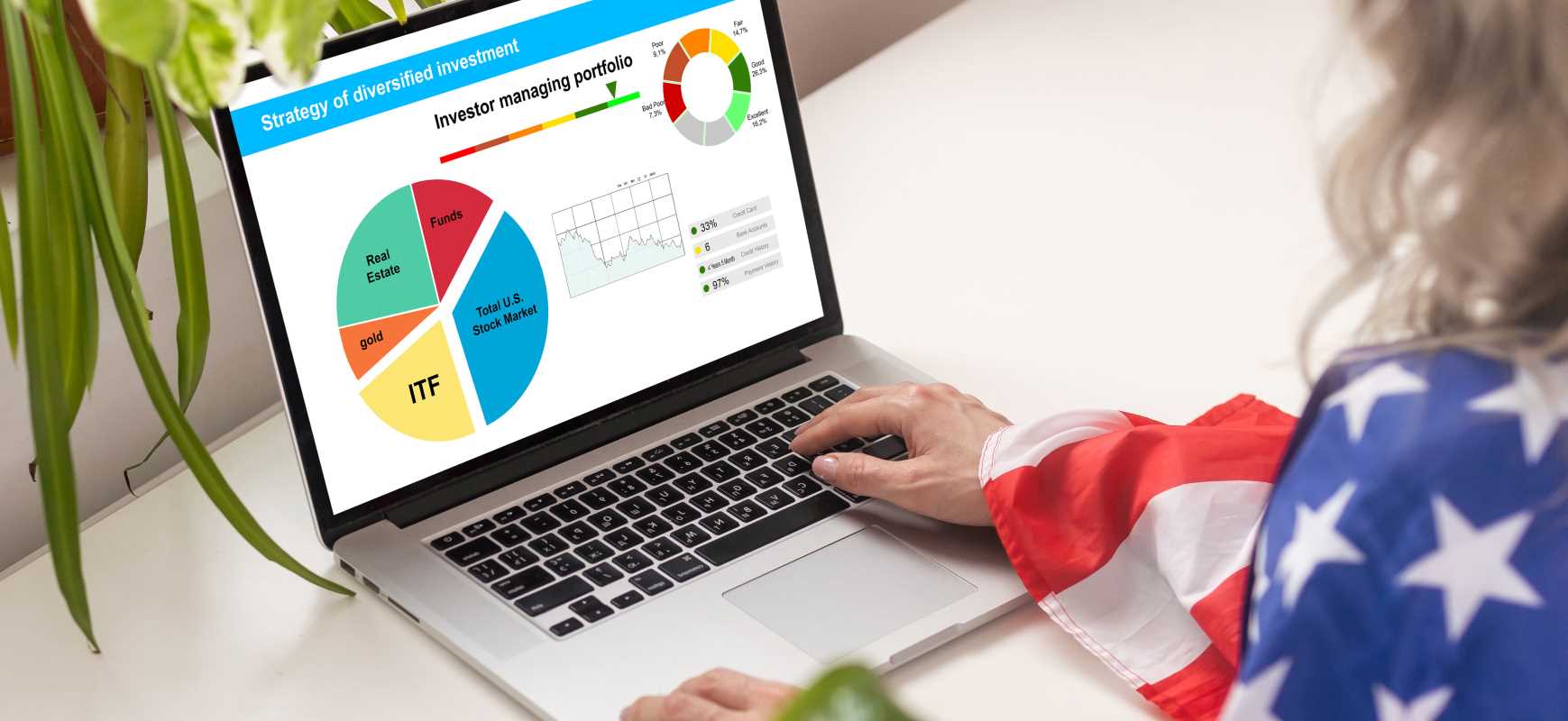
Portfolio diversification is a key strategy for managing investment risk. By spreading investments across various assets, investors aim to reduce the impact of poor-performing assets. While traditional diversification includes stocks, bonds, and commodities, derivatives are increasingly used to enhance diversification. Derivatives are financial contracts whose value depends on an underlying asset, index, or rate. By using derivatives like options, futures, swaps, and forwards, investors can hedge risk, enhance returns, and add flexibility to their portfolios. Understanding their function and role in portfolio diversification is important for modern investors.
What Are Derivatives?
Derivatives are financial instruments whose value depends on the price of an underlying asset. They include options, futures, swaps, and forward contracts. Investors use derivatives for hedging risk, speculation, and arbitrage. For example, a futures contract allows investors to agree to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price in the future, while an option grants the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset. Derivatives help manage risk by offering a way to protect against price fluctuations and to speculate on future price movements without owning the underlying asset.
Types of Derivatives Used in Portfolio Diversification
Several types of derivatives can be incorporated into a diversified portfolio. The most common are options, futures, swaps, and forwards. Each type offers different advantages for risk management and market exposure.
1. Options Contracts
Options contracts provide investors with the right to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price within a specified period. There are two types: call options (the right to buy) and put options (the right to sell). Options help hedge against losses in other investments, especially in volatile markets. For example, purchasing put options can protect against stock price declines, as the value of put options rises when the price of the underlying stock falls. Options are also cost-effective tools for gaining exposure to certain assets without directly owning them. This ability to access various markets makes options an attractive addition to a diversified portfolio.
2. Futures Contracts
Futures contracts obligate investors to buy or sell an asset at a future date for a predetermined price. These contracts are used to hedge against price changes in commodities, stock indices, or currencies. For example, a company that uses oil in its production processes may use oil futures to lock in a price, mitigating the risk of rising oil prices. Futures contracts are useful in portfolio diversification because they enable exposure to markets and assets that are outside traditional equities. Commodities like oil, gold, and agricultural products often perform independently from stocks, offering the potential for diversification.
3. Swaps
Swaps are agreements where two parties exchange cash flows based on different financial instruments. Common types include interest rate swaps, currency swaps, and credit default swaps. In an interest rate swap, one party may exchange a fixed interest rate for a floating rate with another party. Swaps can be used to hedge risks related to interest rates, currency fluctuations, or credit defaults. For example, an investor with exposure to foreign currency risk might use a currency swap to lock in favorable exchange rates, reducing potential losses. Swaps offer more flexibility than futures or options and can be tailored to the specific needs of an investor’s portfolio.
4. Forward Contracts
Forward contracts are private agreements between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a specified future date. Unlike futures contracts, forwards are not standardized and are negotiated directly between the buyer and seller. Forward contracts are commonly used to hedge against risks related to currency fluctuations or commodity prices. In portfolio diversification, forward contracts help manage risks associated with foreign exchange rates or commodity price changes. Investors may use forwards to mitigate volatility or protect against adverse price movements that could impact their portfolio’s value.
How Derivatives Enhance Portfolio Diversification
Derivatives offer several benefits that help improve portfolio diversification. By managing risk, providing access to different asset classes, and potentially enhancing returns, derivatives allow investors to create a more balanced, diversified portfolio.
1. Hedging Against Risk
One of the most important uses of derivatives is hedging. Derivatives like options and futures protect investors from adverse market movements. For example, a portfolio heavy in stocks can use put options to protect against stock price declines. Similarly, futures contracts can lock in prices for commodities or currencies, offering protection against price volatility. Hedging helps reduce the risk of losses from market fluctuations and ensures more predictable returns.
2. Accessing Different Asset Classes
Derivatives make it easier to access a wide range of asset classes, including commodities, currencies, and international markets. These asset classes may not be directly available to all investors, especially those focused on equities and bonds. Futures, options, and swaps provide a means to invest in these areas without the need for direct ownership, enhancing portfolio diversification by adding assets that have a different performance profile than traditional stocks and bonds. For example, a portfolio may gain exposure to agricultural products, energy resources, or precious metals through futures contracts, adding an extra layer of diversification that may not be available through direct investment in these sectors.
3. Amplifying Returns
Derivatives allow for leverage, meaning investors can control larger positions with less capital. This can magnify potential returns when market movements are favorable. For instance, options can provide significant upside potential, as the value of options can increase exponentially if the price of the underlying asset moves in the investor’s favor. However, leverage can also magnify losses if the market moves unfavorably, so it must be used cautiously.
4. Reducing Volatility
By adding derivatives to a portfolio, investors can help reduce overall volatility. Hedging strategies using options or futures can provide downside protection, smoothing out the portfolio’s performance over time. In a market with substantial volatility, derivatives provide a buffer against large swings in portfolio value. This reduction in volatility is particularly important for risk-averse investors or those looking to maintain stable returns.
The Risks of Using Derivatives
While derivatives offer many advantages, they also come with risks. The leverage involved means small market changes can lead to large profits or significant losses. Derivatives can be complex, and their pricing can be influenced by various factors like interest rates, volatility, and time to expiration. Investors must fully understand how derivatives work and carefully manage their use to avoid excessive risk exposure, particularly as they draw closer to retirement.